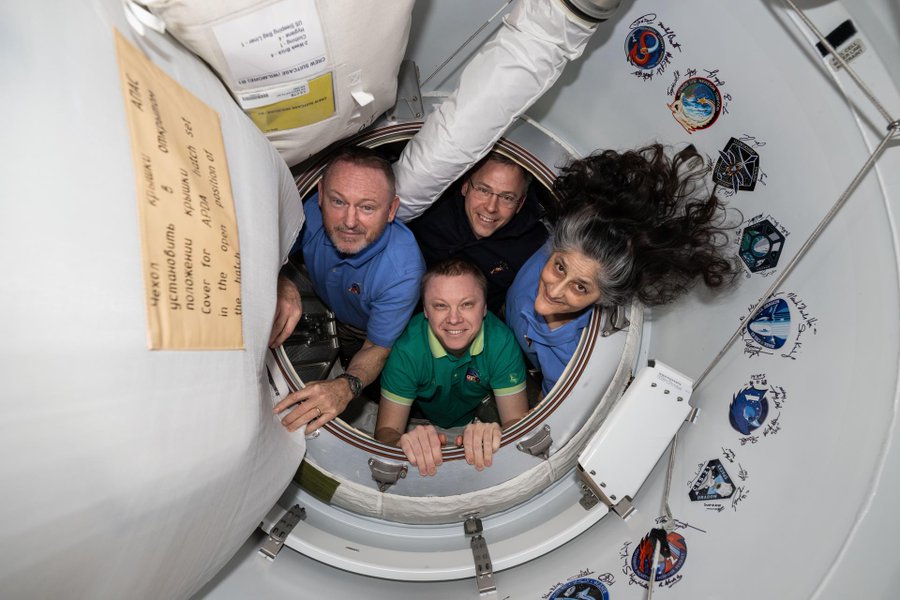
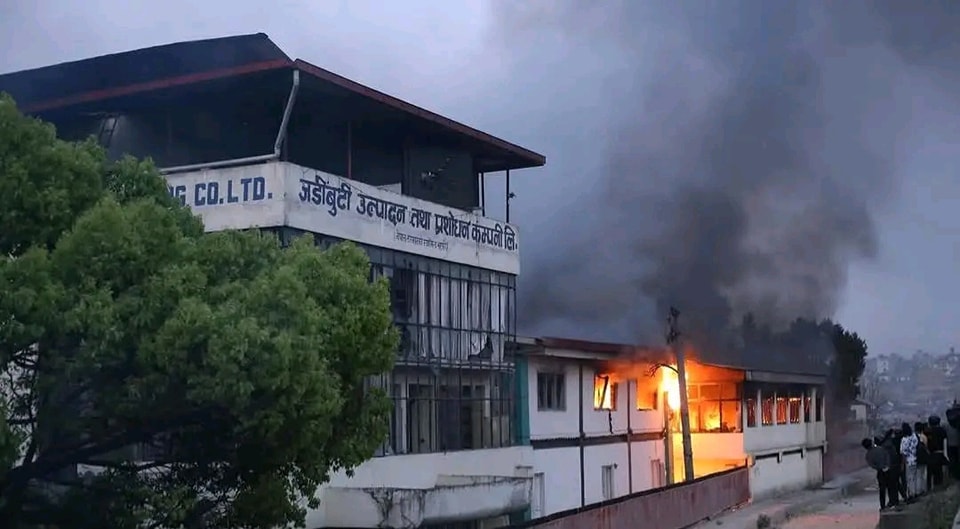
SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft successfully docked at the International Space Station (ISS), carrying NASA astronauts Sunita Williams and Butch Wilmore, along with their crewmates. The mission marks another milestone in space exploration, but it also raises questions about the physical and psychological challenges astronauts face upon returning to Earth.
Life in Space: Challenges and Adaptations
Living in microgravity significantly impacts the human body. Astronauts often experience muscle atrophy, bone density loss, and fluid shifts that can affect vision and balance. Sunita Williams, a veteran astronaut, and Butch Wilmore, a seasoned space traveler, are no strangers to these challenges. However, each mission brings unique adjustments as the body adapts to the lack of gravity.
Returning to Earth: What Changes Await?
Upon their return, Williams and Wilmore may face a period of readjustment. Key changes include:
Gravity Readjustment: After months in microgravity, astronauts often struggle with balance and coordination. Simple tasks like walking or standing can feel overwhelming initially.
Bone and Muscle Recovery: Astronauts lose bone density and muscle mass in space. Intensive physical therapy and exercise are required to regain strength.
Immune System Changes: Prolonged spaceflight can weaken the immune system, making astronauts more susceptible to infections.
Psychological Effects: The transition from the isolation of space to Earth’s bustling environment can be mentally taxing.
The SpaceX mission underscores the complex health challenges associated with space travel. NASA’s comprehensive approach to astronaut health aims to minimize risks and ensure the well-being of its crew members.
swasthyaadmin
Published: March 17, 2025